What is the Wannacry Ransomware Attack?
Have you heard about the WannaCry ransomware attack that caused chaos and wreaked havoc across the globe? If not, then brace yourself for a roller coaster ride of cybercrime drama. This malicious software swept through computer systems like wildfire, encrypting valuable data and demanding hefty sums in return for their release. WannaCry caught everyone off-guard – from healthcare providers to government agencies – leaving them scrambling to protect themselves against this unprecedented threat. In this blog post, we’ll explore what exactly is the WannaCry ransomware attack, how it works, who’s behind it, and most importantly, what you can do to stay safe from such attacks in the future. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is WannaCry Ransomware?
How does WannaCry Ransomware work?
What are the consequences of a WannaCry Ransomware attack?
Who was behind the WannaCry ransomware attack?
How can you protect yourself from a WannaCry Ransomware attack?
Conclusion
What is WannaCry Ransomware?
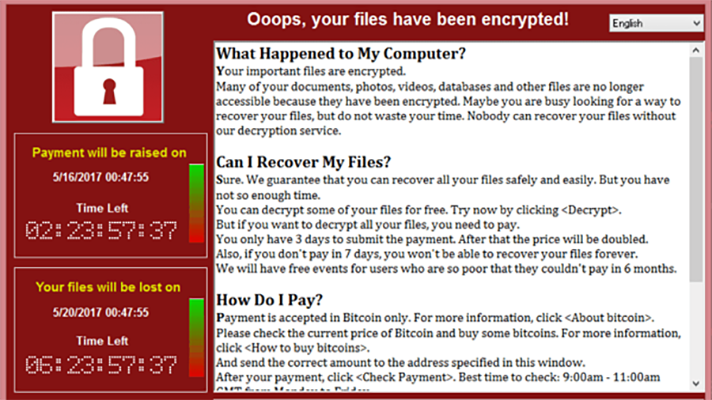
WannaCry ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on your computer, making them unreadable and demanding a ransom to decrypt them. It targets Windows systems, spreading quickly through networks by exploiting a vulnerability in the SMB protocol. WannaCry has caused widespread damage, with over 200,000 computers in 150 countries affected. The attack has primarily hit businesses and organizations, but home users have also been affected. WannaCry has caused billions of dollars in damage and disrupted critical services around the world.
How does WannaCry Ransomware work?
When a computer is infected with WannaCry ransomware, the attacker will encrypt important files on the victim’s machine. Once the files are encrypted, the attacker will demand a ransom from the victim in order to decrypt and return the files. The ransom is typically paid in Bitcoin, which makes it difficult to trace the transaction. In some cases, the attackers have also demanded that the victim pay through a service that allows for anonymous payments, such as Ukash.
WannaCry ransomware uses a number of methods to spread itself, including emails with malicious attachments and exploit kits that exploit vulnerabilities in software. Once a machine is infected, WannaCry will scan for other machines on the same network that are vulnerable to the same exploits and infect them as well. This allows the ransomware to quickly spread across an entire network, making it difficult to contain.
What are the consequences of a WannaCry Ransomware attack?
The WannaCry ransomware attack was a global cyberattack by the WannaCry ransomware cryptoworm, which targeted computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system by encrypting users’ files and demanding ransom payments in the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. The attack began on 12 May 2017 and spread rapidly across 150 countries, affecting more than 200,000 victims.
The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom was particularly affected, with 47 NHS organizations reporting that they had been infected. The attack caused delays in treatment and appointments at hospitals and GP surgeries across the country. There were also reports of cancelled operations.
The WannaCry ransomware encrypted files on victims’ computers, making them inaccessible. It demanded a ransom of $300 worth of Bitcoin for each computer, to be paid within three days. If payment was not made within that time, the price doubled to $600 worth of Bitcoin. After seven days, the files would be permanently deleted.
The WannaCry attacks highlighted a number of vulnerabilities in computer systems. One was the use of outdated software: many of the computers affected by WannaCry were running Windows XP, an operating system that was first released in 2001 and is no longer supported by Microsoft (although Microsoft did release a patch for Windows XP after the attack). Another vulnerability was the use of unsecured RDP connections: WannaCry exploited a flaw in Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to spread itself across networks. RDP is a feature that
Who was behind the WannaCry ransomware attack?
In May 2017, a ransomware attack known as WannaCry hit computers around the world. The attack locked users’ files and demanded a ransom be paid in order to unlock them. According to estimates, the attack affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries.
The WannaCry attack was made possible by a vulnerability in Microsoft’s Windows operating system. The vulnerability was first discovered by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) and was then leaked online by a group called the Shadow Brokers.
Once the Shadow Brokers leaked the NSA’s tools, it didn’t take long for someone to create an exploit that could be used to launch attacks like WannaCry. While it’s not clear who was behind the initial WannaCry attack, researchers believe that the attackers were likely not very sophisticated and may have simply been taking advantage of the fact that many people had not yet patched their systems to protect against the Windows vulnerability.
How can you protect yourself from a WannaCry Ransomware attack?
In May of 2017, a ransomware attack known as WannaCry hit computer systems around the world. The WannaCry attack infected over 200,000 computers in 150 countries and caused billions of dollars in damage. The attack was stopped by a security researcher who found and activated a kill switch in the code. However, the WannaCry attack showed us just how vulnerable our computer systems are to ransomware attacks.
So, how can you protect yourself from a WannaCry ransomware attack?
First, make sure that your operating system and all software is up to date. Cyber criminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. By keeping your software up to date, you can close these vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Second, install and maintain reliable anti-virus and anti-malware software on your computer. These programs can detect and remove malware before it has a chance to encrypt your files.
Third, back up your important files regularly. That way, even if your computer is infected with ransomware, you will not lose your data. Store your backups offline (not on your computer) so that they cannot be encrypted by ransomware.
Fourth, be cautious when opening email attachments or clicking on links in emails. This is one of the most common ways that ransomware is spread. If you receive an email from someone you don’t know or an unexpected attachment, do not open it! And if you receive an email with a link
Conclusion
The WannaCry ransomware attack is an example of the real-world risks and damages that cyberattacks can cause, both to individuals and organizations alike. Cybersecurity measures such as data encryption, two-factor authentication, and regular backup practices are necessary for everyone in this digital age to protect themselves against malicious actors like those responsible for the WannaCry attack. By staying up-to-date on the latest security best practices and staying vigilant about our online activities, we can all do our part to make sure these types of attacks never happen again.



